Project Planning
The overall goal of the GPP is to accelerate the field of functional genomics, the toolkit of experimental approaches for understanding gene function. To fulfill this mission, we partner with scientists in the Broad community and beyond on their biological question of interest, engaging in the project from conception to analysis to publication.
Our expertise includes inherent challenges, pitfalls, and optimization guidelines that are not always obvious - this technical information, and years of experience seeing common challenges across projects, often makes the difference between a good idea and a successful experiment. Continued engagement will also ensure that a project has access to cutting-edge tools and methodologies we develop far in advance of publication.
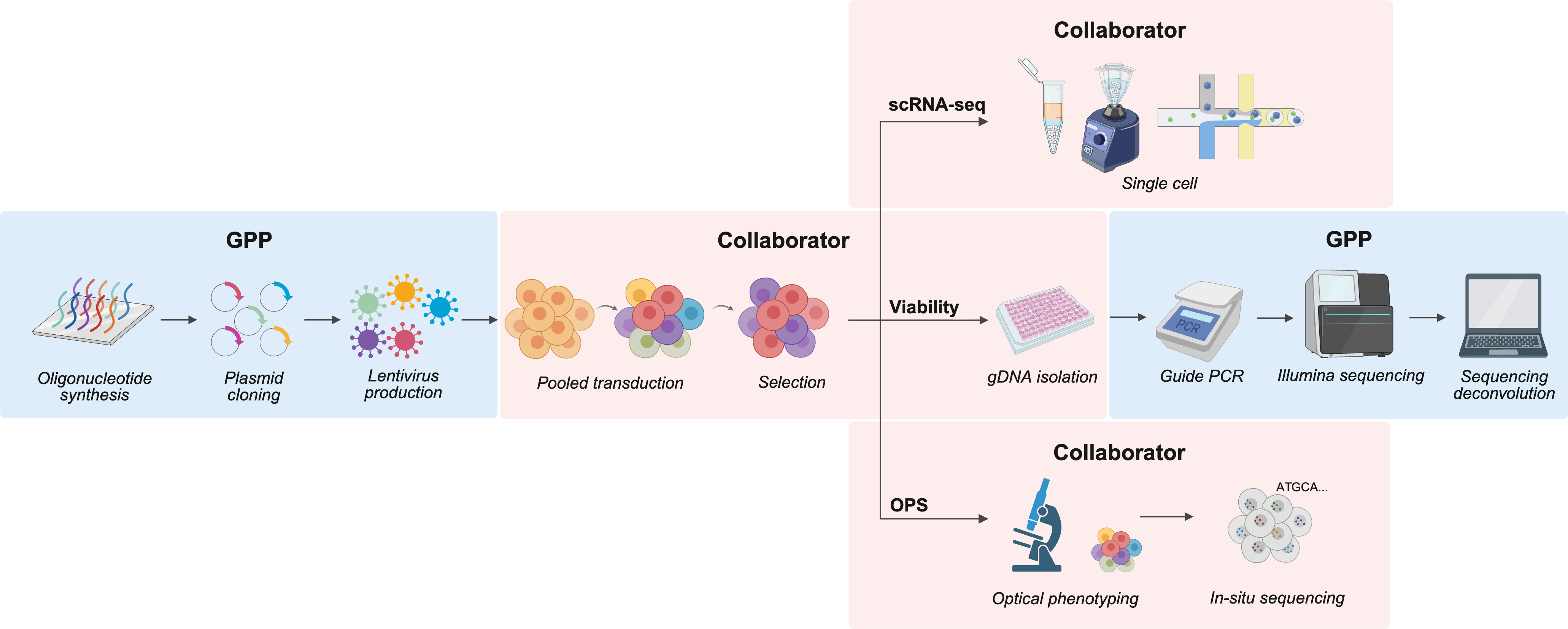
Reviewing our GPP Collaboration Guide and scheduling an introductory meeting with one or more GPP screening scientists is a good place to start. Below is a depiction of a typical collaboration using a pooled screening approach, but please note that we also support single-cell RNA sequencing and optical pooled screening readouts.
Reagents
To aid in conceptualizing a screen, we provide an overview of our most commonly-used reagents. Click on ‘Inventoried’ or ‘Customized’ to read more about GPP's reagents. Please note that this is not an exhaustive list and further discussion with your screening scientist(s) is often helpful.
GPP maintains a collection of pooled CRISPR libraries across modalities - knockout, activation, and interference - as well as a human open reading frame (ORF) library:
- Selecting a Genome-Wide Library
- Guidance on genome-wide libraries and considerations across the numerous CRISPR modalities
- Druggable CRISPR Libraries
- Additional details for a suite of libraries targeting genes annotated as druggable from the Pharos project
A full list of existing pooled libraries: Browse existing libraries
Instructions for acquiring these reagents can be found here: Ordering Pooled Libraries
GPP also maintains individual (arrayed) reagents that can be provided as bacterial streaks and/or plasmid DNA and/or lentivirus:
FAQs:
Q: If thinking about an in vivo screen, are there additional resources?
Indeed. Maintaining coverage in an in vivo setting often requires specific experimentation. Cell Counter Libraries can be used for this purpose.
Alternatively, you may consider adding iBar UMIs to your library.